The Evolution of Anesthesia Techniques
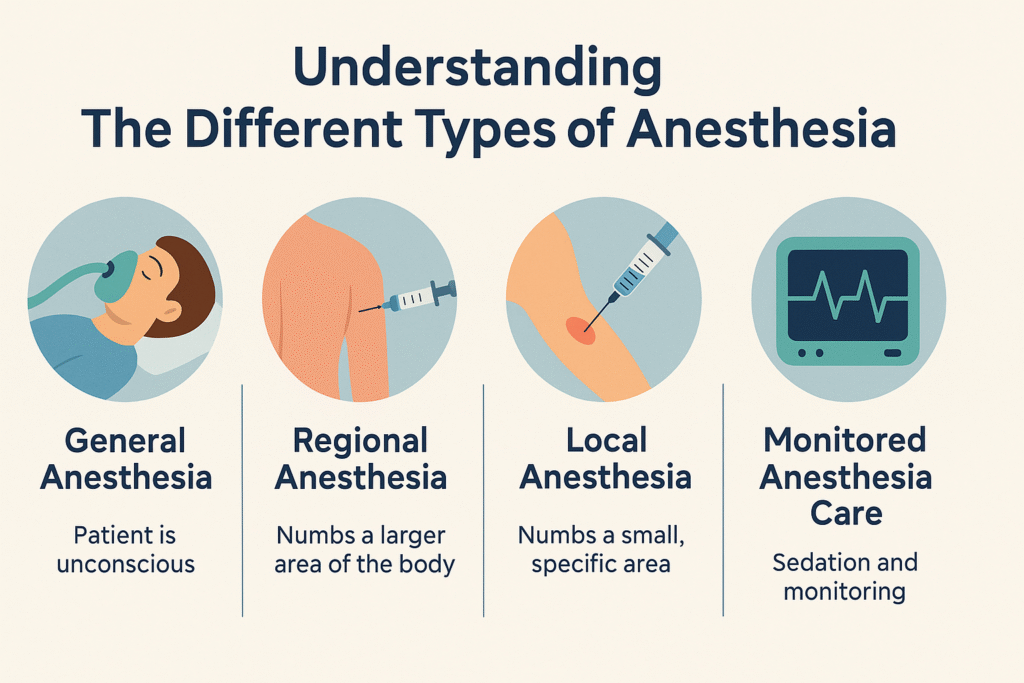
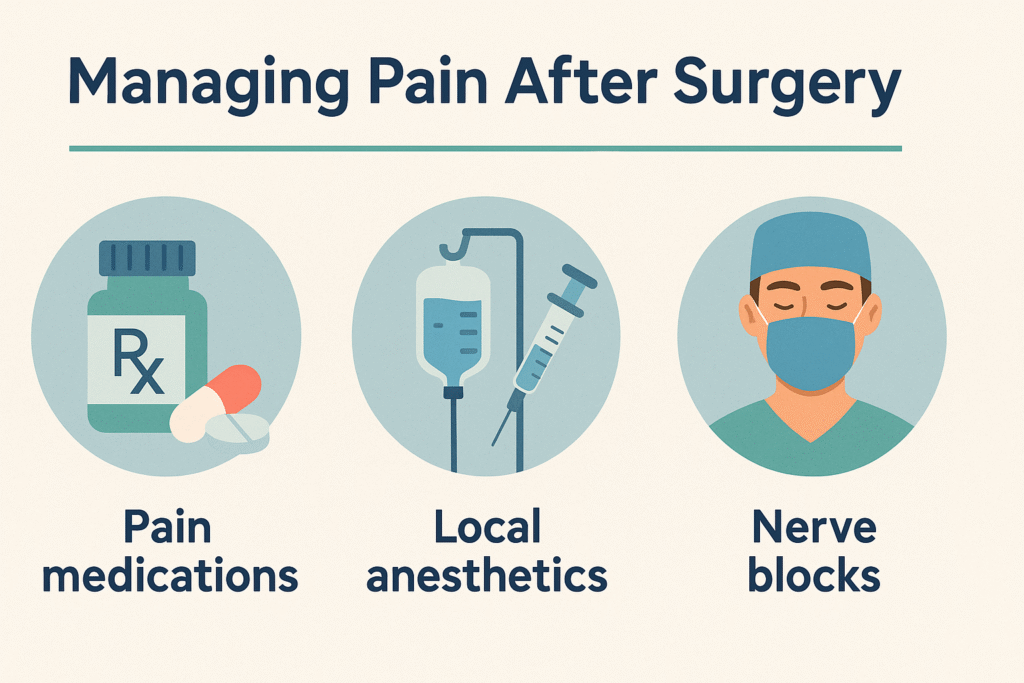
The evolution of anesthesia techniques represents a fascinating journey through medical history, marked by innovation, experimentation, and a deepening understanding of the human body’s response to pain. Here’s a chronological overview of key milestones in the development of anesthesia techniques: There are several types of anesthesia, each tailored to the specific needs of the patient and the nature of the procedure: Early Herbal Remedies Ancient civilizations, such as the Egyptians and Greeks, utilized herbal concoctions containing substances like opium, mandrake, and henbane for their sedative and pain-relieving properties. These early remedies laid the foundation for later developments in anesthesia. Ether and Chloroform In the early 19th century, the discovery of ether and chloroform revolutionized surgical practice. In 1846, American dentist William T.G. Morton famously demonstrated the use of ether as an inhalation anesthetic during a surgical procedure at Massachusetts General Hospital. Chloroform, introduced shortly afterward by Scottish obstetrician James Young Simpson, also gained popularity as an anesthetic agent. Local Anesthesia The advent of local anesthesia, which blocks pain sensation in a specific area of the body without affecting consciousness, represented another significant milestone. In 1884, Austrian ophthalmologist Carl Koller discovered the anesthetic properties of cocaine when applied topically to the eye, leading to the widespread use of local anesthesia in various medical procedures. Regional Anesthesia Building upon the concept of local anesthesia, physicians began exploring techniques to block pain transmission along larger nerve pathways. Spinal anesthesia, pioneered by German surgeon August Bier in 1898, involved injecting local anesthetic into the cerebrospinal fluid surrounding the spinal cord. Epidural anesthesia, introduced later, provided a similar effect by injecting anesthetic into the epidural space outside the spinal cord. Intravenous Anesthesia The development of intravenous anesthetics, such as thiopental and propofol, offered an alternative to inhalation agents for inducing and maintaining general anesthesia. Intravenous anesthesia became increasingly popular due to its rapid onset of action and precise control over the depth of anesthesia. The evolution of anesthesia techniques reflects centuries of ingenuity, experimentation, and scientific progress in the quest to alleviate pain and ensure the safety and comfort of patients undergoing surgical procedures. Today, anesthesia continues to evolve with ongoing research, technological advancements, and a commitment to optimizing patient outcomes and satisfaction All these facilities related to Obstetric Anaesthesia & Analgesia, Anaesthesia for Laparoscopic Surgeries are available in Naval Nursuring Home near Railway line, Dutta chowk, Solapur Remember, this blog post is for informational purposes only, and it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional. More Blogs The Role Anesthesiologists in Surgical Care Introduction: Surgical procedures require a multidisciplinary approach to ensure patient safety and Read More The Evolution of Anesthesia Techniques The evolution of anesthesia techniques represents a fascinating journey through medical history, Read More The Role of Anesthesiologists in Patient Safety and Comfort During Surgery Ex audire suavitate has, ei quodsi tacimates sapientem sed, pri zril ubique Read More Understanding The Different Types of Anesthesia There are four main categories of anesthesia used during surgery and other Read More
The Evolution of Anesthesia Techniques Read More »